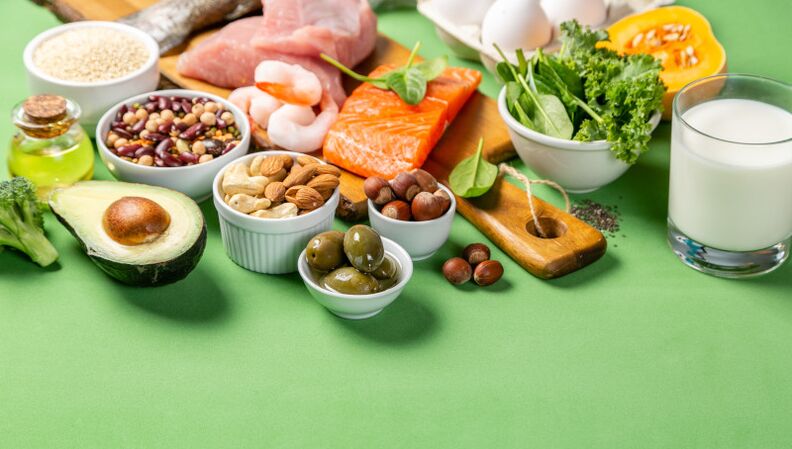
The Mediterranean diet is a diet with a special reputation; in fact, it is a nutritional system that allows you to improve your health and, as a bonus to protect you from cancer and cardiovascular disease, achieve a slim figure. It is tasty, balanced and varied. The dishes of this diet are rich in carbohydrates, a large amount of fish and seafood, all seasoned with aromatic spices and olive oil, accompanied by a glass of red wine. Complete foodie! You can also use the Mediterranean diet to lose weight, although many people associate the countries of this region with pizza and pasta.
Diet for long life

The term "Mediterranean diet" was first introduced to the world thanks to American nutritionists Ansel and Margaret Keys, who ate according to the principles of the Mediterranean diet since the 1940s and lived no less than 97 and 100 years each. It is the only diet in the world to receive UNESCO Intangible Cultural Heritage status in 2013. Today, the Mediterranean diet is especially popular among celebrities Victoria Beckham, Cameron Diaz, Eva Longoria and Jennifer Aniston.
There is only one drawback: this approach to healthy eating should be followed throughout life, but, nevertheless, since the mid-90s the diet has more and more fans.
Why "Mediterranean"? Studies have shown that the attractiveness, longevity and good health of the inhabitants of Greece, northeastern Spain, Italy, Portugal, southern France and other countries of the Mediterranean region directly depend on their approach to a healthy diet.
Basic principles of diet
The carbohydrate, protein and fat content in the diet is 60%, 10% and 30% respectively. But the main secret is that fats and carbohydrates in the diet for weight loss must be correct. That is, durum wheat pasta, legumes and many types of wholemeal bread. Also olive oil, avocado, fatty fish. Add to this a salad of fresh vegetables and herbs and a healthy lunch is on the table.
At the same time, there are no restrictions or rigid methods, because the fundamental principle of the system is that the products are divided into:
- included in the daily diet;
- consumed 1-4 times a week;
- allowed no more than 1-2 times a month.
Green
Each country has its own preferences when it comes to greens, but there is a lot of it on the tables.
Therefore, the Greeks use lettuce leaves as "green pita bread", wrapping vegetables, meat and cereals in them. Horta is a popular snack: a mixture of herbs with butter or lightly fried.
Love for spinach comes from France, its neutral taste allows you to use vegetables both as a main dish and as a filling of all kinds in culinary delights.
And Italians love broccoli, and the healthiest part is the leaves, which they eat raw, balancing the spicy taste with tomato and cheese, and fried, seasoned with balsamic vinegar.
Dairy products
Dairy products are consistently popular in Mediterranean countries. When used correctly, animal milk is a source of calcium, vitamin D, proteins and amino acids. And, if France is a fan of hard and mature cheeses, then Greece is a true lover of yoghurts. There they are served with salads, meat, bread products and as independent dishes, with or without fruits, herbs.
In the first rows of benefits among cheeses we find:
- Dietary goat's cheese, low in calories, but rich in B vitamins, microelements and easily digestible proteins.
- Feta made from sheep or goat's milk helps control blood pressure, calms the nervous system and gives strength to bones.
- Spicy Parmesan is a leader in protein, vitamin and amino acid content.
- Silky provolone is also enriched with enzymes beneficial to humans, which give it an unusual taste.
Vegetables
The variety of salads on the menu is quite expected in Mediterranean countries. Nutritionists have always emphasized the need for an abundance of vegetables in the daily diet. This will help improve digestion and heart function. Fresh vegetables with minimal processing, olive oil, the spicy flavor of aromatic herbs. . . And on your table there is a source of vitamins, organic acids, carbohydrates, proteins and fats - everything the body needs. Add a couple of slices of feta - this is what an authentic Greek salad looks like, the hallmark of Mediterranean cuisine.
Meat and fish
If we analyze the ratio of meat and fish dishes, then, despite delicacies such as Italian Parma ham or Spanish jamon, fish and seafood still dominate. Red meat is rarely found on the menu, because it is from seafood that the maximum amount of saturated fatty acids, vitamins and microelements is obtained.
Fats
An important feature of the Mediterranean diet is the reduction of saturated animal fats in favor of healthier vegetable oils and unsaturated fats. Vegetable oils are olive oil, nuts, seeds. Unsaturated fats predominate in fatty fish with the highest content of omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids. It helps maintain the balance of vitamins and microelements in the body and the benefit will be elastic skin and shiny hair.

Olive oil
Olive oil holds a special place on the menu of the Mediterranean diet. A few tablespoons of oil a day is a must in this unique approach to healthy eating. Don't be alarmed: some nutritionists recommend eating 60 grams a day for breakfast. soaked bread 40 gr. olive oil. This is not surprising, because the fats in olive oil are similar to the fats in breast milk, so it is recommended to start with it to introduce vegetable oils into complementary foods. For an adult gourmet, olive oil improves bone mineralization, improves digestion and stabilizes blood pressure. Olive oil contains oleic acid (up to 70% by volume). It belongs to Omega-9 unsaturated fatty acids and acts as a powerful natural antioxidant. As a result, the metabolism improves and the aging process slows down. Olive oil also contains many vitamins E and K, which help improve immunity and regulate the body's energy processes.
You should also understand that not all olive oil is produced according to the rules. Many unscrupulous manufacturers fill the market with counterfeit and low-quality products. These oils can be extracted and processed inappropriately, which destroys delicate nutrients, and some fatty acids can even become rancid or toxic. Therefore, you should choose only high-quality oil, with markings on the labelextra virginand, ideally, cold pressed. After all, the peculiarity of olive oil is that it can be consumed raw without any processing. Those who are lucky enough to grow olives on their territory can press the olives by hand and enjoy the finest natural oil.
Spices, condiments, aromatic oils
Mediterranean cuisine is particularly enriched with aromatic oils infused with herbs and seasonings. You can easily prepare them at home on your own: oil infused with garlic will harmoniously decorate pasta and sauces, mint oil will emphasize the freshness of salads, and lemon oil will add sophistication to fish dishes. At the same time, salt consumption is significantly reduced, which also explains the healing effect on the cardiovascular system in particular and the entire body as a whole. Feel free to use spices and seasonings in your recipes, experiment with combinations and dosage.
Red wine
There is also a spicy feature to the diet: red wine is encouraged, although moderate alcohol consumption is emphasized. 10 to 50 ml per day is enough to improve heart function, clean blood vessels and simply have a good mood.
Benefits of the Mediterranean Diet
- Products for this diet are minimally processed and without additional refined sugar.
This includes olive oil, fruits and vegetables, legumes, nuts, whole grains, and small portions of animal products, which are necessarily "organic" and not shelf-stable. There are virtually no GMOs, artificial ingredients, preservatives, flavor enhancers and very little sugar. For desserts, Mediterranean people use fruit or light homemade desserts using natural sweeteners such as honey.
The animal component of the diet is represented by the moderate consumption of cow, goat or sheep cheeses and yogurt and lots of locally caught fish. This is a source of omega-3 fatty acids and other healthy fats, the "correct" cholesterol, which strengthens the walls of blood vessels.
- Improvement of the cardiovascular system
High intakes of monounsaturated fats and omega-3 foods are associated with significant reductions in all-cause mortality, particularly heart disease. Many studies have demonstrated the positive effects of a Mediterranean diet rich in alpha-linolenic acid (ALA) from olive oil, including a 30% reduction in the risk of death from cardiovascular disease, as well as a 45% reduction in acute heart failure.
Warwick Medical School also found that people who regularly consumed extra virgin olive oil experienced greater blood pressure reductions than people who predominantly consumed sunflower oil.
Furthermore, it is extremely rare for Mediterranean populations to have low levels of "good" cholesterol because they routinely get plenty of healthy fats from their natural diet.
- Lose weight healthily
With this diet you can eat a very varied and tasty food without feeling hungry. You will therefore be able to follow this diet for a long time without interruptions, regulating your weight and reducing your fat intake in a simple and natural way. There is room for variation in the Mediterranean diet, whether you prefer to increase the amount of carbohydrates or emphasize high-quality protein products from animal and, especially, plant-based sources. In any case, this eating style will help regulate weight gain, control blood sugar levels, improve mood and maintain consistently high energy levels.
- Cancer prevention
According to researchers from the Department of Surgery at the University of Genoa in Italy, a balanced ratio of omega-6 and omega-3 essential fatty acids, a high content of fiber, antioxidants and polyphenols found in fruits, vegetables, olive oil and wine, protects DNA protects against damage and stops cell mutation, reduces inflammatory processes and delays tumor growth. Olive oil also reduces the risk of colon and bowel cancer.
- Treatment and prevention of diabetes
The Mediterranean diet controls excess insulin, the hormone that controls blood sugar, makes us gain weight and maintains our weight even during the diet.
There is ample evidence to suggest that the Mediterranean diet may serve as an anti-inflammatory diet that can help fight diseases associated with chronic inflammation, including metabolic syndrome.
A diet low in sugar and rich in fresh, fatty foods is part of the natural lifestyle of diabetics.
A Mediterranean eating style helps prevent blood sugar spikes and drops. Carbohydrates - in the form of wholemeal bread or durum wheat pasta, often paired with olive oil or cheese, plenty of greens and greens - are an excellent source of energy for several hours without significant spikes in sugar levels and an early sense of hunger.
- Protect cognitive health and promote good mood
Healthy fats like olive oil and walnuts are known to help fight age-related cognitive decline. They can counteract the harmful effects of toxicity, free radicals, poor inflammatory diets, or food allergies that can contribute to brain dysfunction. Cognitive disorders can occur when the brain does not receive enough dopamine, an important chemical needed for proper body movement, mood regulation and mental functioning.
Probiotic foods like yogurt and kefir promote healthy gastrointestinal function, which has also been linked to cognitive function.
Therefore, the Mediterranean eating style can be a natural treatment and prevention for Parkinson's disease, Alzheimer's disease and age-related dementia.
- Promotes longevity
In 1988, a study conducted in Lyon asked heart attack patients to follow a Mediterranean diet rich in monounsaturated fats or a standard diet with a significant reduction in saturated fats. Four years after the study began, results of a follow-up exam showed that patients in the first group were 70 percent less likely to suffer from heart disease and also had a lower risk of death from any cause by 45% compared to the group with a standard diet. At the same time, no significant difference was found in the level of total cholesterol, which demonstrated the absence of a direct relationship with heart disease. The results were so impressive and groundbreaking that, for ethical reasons, the study was stopped early so that all participants could continue to eat a Mediterranean diet for maximum health and longevity.
- Helps relieve stress and relax
Chronic stress significantly reduces quality of life and negatively affects weight and overall health. The Mediterranean diet encourages you to spend more time in nature and get a good night's sleep. This is a great way to relieve stress and therefore prevent inflammation. Plus, there's more time to laugh, dance, relax and enjoy hobbies.
- Fights depression
A study published in the Journal of Molecular Psychiatry in 2018 found that following a Mediterranean diet reduces the likelihood of depression. Inflammation is often cited as a root cause of many psychiatric disorders and conditions, including schizophrenia, obsessive-compulsive disorder, depression, anxiety, fatigue, and social withdrawal. A nutrient-rich diet, on the other hand, helps protect the brain from organic and functional changes. Other diet and lifestyle changes, such as getting enough sleep, being mindful of what you eat, choosing your menu in advance, and limiting stress, lead to stable mental health.




What is possible and how often
If you decide to try this popular and in many ways unique food system, from now on you should have the following products on your table every day:
- Fresh fruit (apples, bananas, pears, citrus fruits, figs, peaches, apricots, berries, melons, watermelons);
- Vegetables (mainly non-starchy ones, such as tomatoes, eggplants, artichokes, all types of cabbage), greens (especially leafy ones - spinach, lettuce);
- Whole grain products (brown rice, rye, barley, corn, buckwheat, whole oats, wheat and products made from them - bread and pasta);
- Legumes and beans (lentils, chickpeas, beans, peas, peanuts);
- Root vegetables (yams - sweet potatoes, turnips, sweet potatoes, parsnips, Jerusalem artichokes);
- Nuts and seeds (walnuts, almonds, hazelnuts - hazelnuts, macadamia nuts, cashews, sesame seeds, sunflower seeds, pumpkin seeds);
- Spices and herbs (garlic, nutmeg, cinnamon, pepper, basil, mint, rosemary, sage) will allow you to minimize the amount of salt in your diet;
- Vegetable fats (olive oil, pure avocado and oil from it);
- Pure water, approximately 2 liters per day, tea or coffee are allowed, but sugary drinks and fruit juices should be avoided;
- Dairy products - cheese, yogurt or kefir - in moderation;
- Red wine in moderation (but this is completely optional).
Every week you need:
- Fish and seafood (give preference to wild fish varieties over artificially grown ones), shrimp, oysters, clams, mussels, crabs - at least 4 times a week;
- Eggs – in moderation, 2-4 times a week;
- Potatoes – in moderation;
- Some sweets.
Every month you can eat:
- Red meat;
- Poultry (chicken, duck, turkey) and lean meat (rabbit, ham, pork fillet).
You should avoid in your diet:
- Refined sugar and products containing it (ice cream, sweets, drinks, table sugar);
- Highly processed cereals (white bread, wheat pasta, polished cereals);
- Trans fats (margarines and products containing them);
- Refined oils (all types, including soybean, canola, cottonseed);
- Processed meat products (sausages, sausages, semi-finished products);
- Products that have undergone further processing or enrichment (labeled "low-fat", "enriched", "refined").
Menu of the week
A huge advantage, but at the same time also a disadvantage, of the Mediterranean nutritional system is the absence of strict rules and a clear nutritional plan. To help you orient yourself, here is the menu of the week, adapted to the food basket of our strip.
Monday
- Breakfast – yogurt with cereals and berries.
- Lunch: cabbage soup and roast meat.
- Dinner – vegetable salad with eggs, dressed with olive oil and lemon juice.
- Snacks – seasonal fruit salad, a handful of nuts.
Tuesday
- Breakfast: oatmeal with flax seeds, honey and banana slices.
- Lunch – lasagna with vegetables.
- Dinner: Baked eggplant with feta cheese and cheese sandwich.
- Snack: probiotic yogurt, grapes and popcorn.
Wednesday
- Breakfast: berry pudding prepared with Greek yogurt and chia seeds.
- Lunch: wholemeal sandwich with vegetables.
- Dinner: Grilled salmon served with brown rice and vegetables.
- Snack: toasted pumpkin seeds, celery with peanut butter.
Thursday
- Breakfast: omelette with tomatoes, peppers, onions, broccoli and feta.
- Lunch – spinach soup with sour cream, cream or Greek yogurt, baked potatoes.
- Dinner: Shrimp salad, dressed with olive oil.
- Snack: assorted tropical fruit, carrots with hummus.
Friday
- Breakfast: Oatmeal with dried fruit and nuts.
- Lunch: vegetable soup with chicken broth.
- Dinner – fried or baked fish.
- Snacks: kale or zucchini chips, olives.
Saturday
- Breakfast – Sweet potato casserole with spinach and cheese.
- Lunch – Wholemeal Mediterranean pizza with cheese, vegetables and olives.
- Dinner – salmon with buckwheat, cabbage salad.
- Snacks: fruit, cottage cheese with dried fruit.
Sunday
- Breakfast: yogurt with bifidobacteria with chopped fruit and nuts.
- Lunch: tuna salad dressed with olive oil.
- Dinner - Greek salad with cucumbers, tomatoes, black olives, spinach, feta cheese, dressed with olive oil, a piece of lean steak.
- Snack: assorted nuts, fruit salad.
Disadvantages and harms of the diet
The disadvantage of this food system is, first of all, the need to change one's eating habits: abandon many processed and refined products in favor of high quality and, often, expensive products. Furthermore, it is not yet known which factor will be more significant: the high cost or the previous diet habit.
Also, this diet may not be suitable for people with individual intolerances and allergies to seafood. People with stomach and intestinal ulcers should approach the choice of menu with caution, given the high fiber content in the daily menu. It is also worth avoiding dietary red wine for pregnant women and other people for whom alcohol, even in small quantities, can be harmful.

Lose weight with the Mediterranean diet
Many people doubt whether it is possible to lose weight on such a diet? In fact, this gentle diet does not give immediate results, so it is not suitable for correcting severe obesity. If the main goal of the diet is weight loss, then you should definitely include physical activity. Not all diets associated with dietary restrictions allow you to fully train. And here there is a pleasant plus: it is the Mediterranean diet that gives you the strength to exercise. This improves weight loss results, creates a beautiful and fit figure and improves health.
Those who have decided to lose weight using this method may find the lack of a strict menu inconvenient. You will have to calculate yourself how many calories you need in order not to feel hungry, but at the same time lose weight, and independently correlate physical activity and the amount of food consumed. However, most dieters find it convenient, because strict restrictions are harder to achieve.
Summary
The Mediterranean diet is not a diet in the usual sense of the term, but a specific nutritional system that a person can stick to for life. It's important to provide three nutritious meals and two snacks throughout the day so you don't go hungry. It is thanks to the unique diet: high consumption of olive oil, fruits, nuts, vegetables and cereals; moderate consumption of fish and poultry; low consumption of dairy products, red meat and sweets; and red wine in moderation – reduce rates of chronic disease on the path to longevity.